
Email Signing that can be signed and encrypted when sending e-mails.
Email Signing S/MIME Certificates
Email certificates provide the strongest levels of confidentiality and security for your electronic communications by allowing you to digitally sign and encrypt your mail and attachments.
How does it works?
S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) is a protocol that adds security and privacy features to email messages. It enables the encryption, authentication, and integrity checking of email content, ensuring that messages are protected during transit and verifying the identities of the sender and recipient.
Here's a simplified explanation of how S/MIME works:
1. Obtaining a digital certificate: To use S/MIME, both the sender and recipient need to obtain a digital certificate from a trusted certificate authority (CA). The certificate contains their public key and identifies them as a trusted entity. The certificate is typically installed in their email client or stored on a cryptographic device.
2. Digital signature: When the sender wants to send an email, their email client uses their private key (paired with the public key in their certificate) to create a digital signature. The signature is a unique cryptographic code generated based on the content of the email. It ensures the integrity of the message, allowing the recipient to verify that the email hasn't been tampered with during transit.
3. Encryption: If the sender wants to encrypt the email for confidentiality, they obtain the recipient's public key from their certificate. The email client then encrypts the message content using the recipient's public key, ensuring that only the intended recipient can decrypt and read the message.
4. Verification and decryption: When the recipient receives the email, their email client uses the sender's public key (obtained from their certificate) to verify the digital signature. This ensures that the email has not been modified during transit and that it was indeed sent by the claimed sender.
5. Privacy and confidentiality: If the email was encrypted, the recipient's email client uses their private key (paired with the public key in their certificate) to decrypt the email and reveal the original message content.
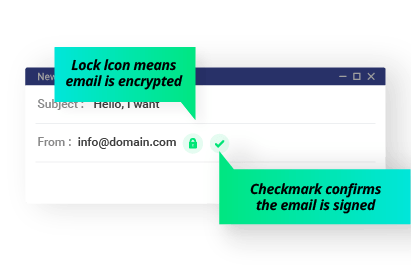
By combining digital signatures and encryption, S/MIME provides end-to-end security for email communication. It allows users to ensure the authenticity of messages, protect their content from unauthorized access, and maintain the privacy of their communications.
It's worth noting that S/MIME requires both the sender and recipient to have valid digital certificates and compatible email clients that support the protocol.